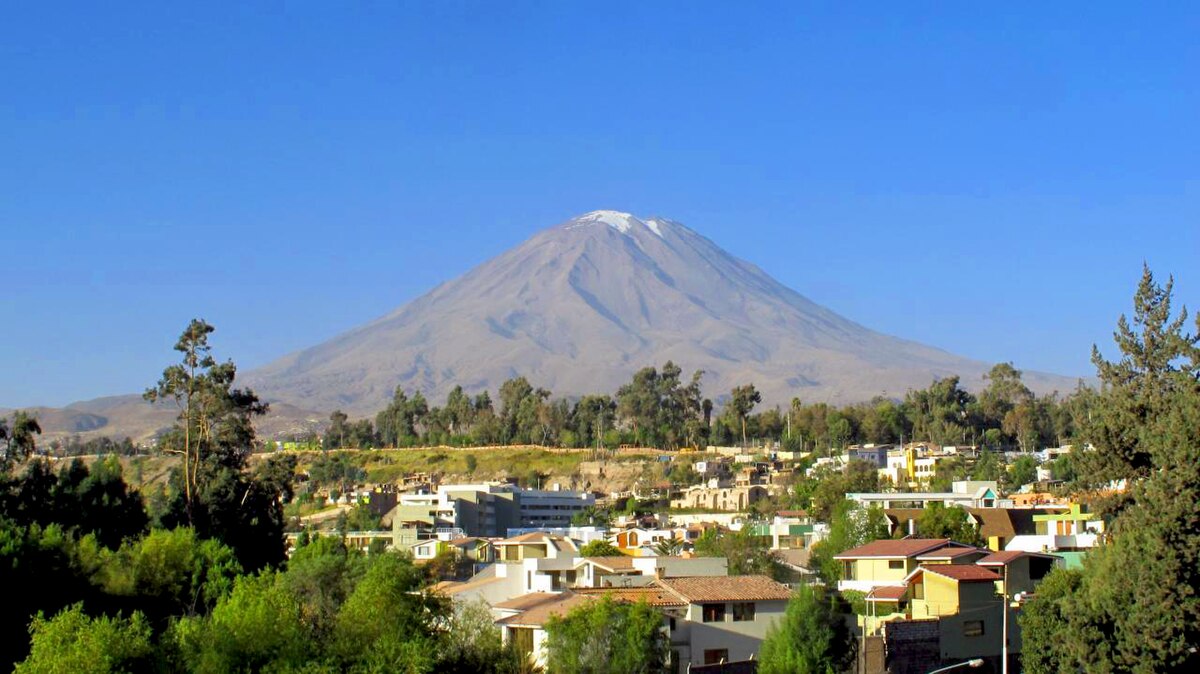
If you’re planning to visit Arequipa and embark on a beautiful adventure, climbing the majestic Misti volcano could be the perfect experience for you. Standing at 5,822 meters above sea level, Misti is one of the most famous volcanoes in Peru, known not only for its imposing presence but also for its cultural significance and appeal to mountaineers.
Here at Machu Picchu Wayna, we share everything you need to know about the Misti volcano—from its history and location to how to get there, what to bring, and the best tips to fully enjoy this unique experience.
Description of Misti Volcano
Misti is a stratovolcano and one of over 16 volcanoes in Peru, characterized by its conical shape and snow-capped summit during the colder months. Its silhouette is a symbol of the city of Arequipa and can be seen from almost anywhere in the city.
In Quechua, “Misti” means “lord of the white race.” Volcanic activity here is moderate, and although its last significant eruption occurred more than 500 years ago, it remains active and is constantly monitored by professionals. Its iconic shape makes it an attractive destination for both tourists and mountaineers.
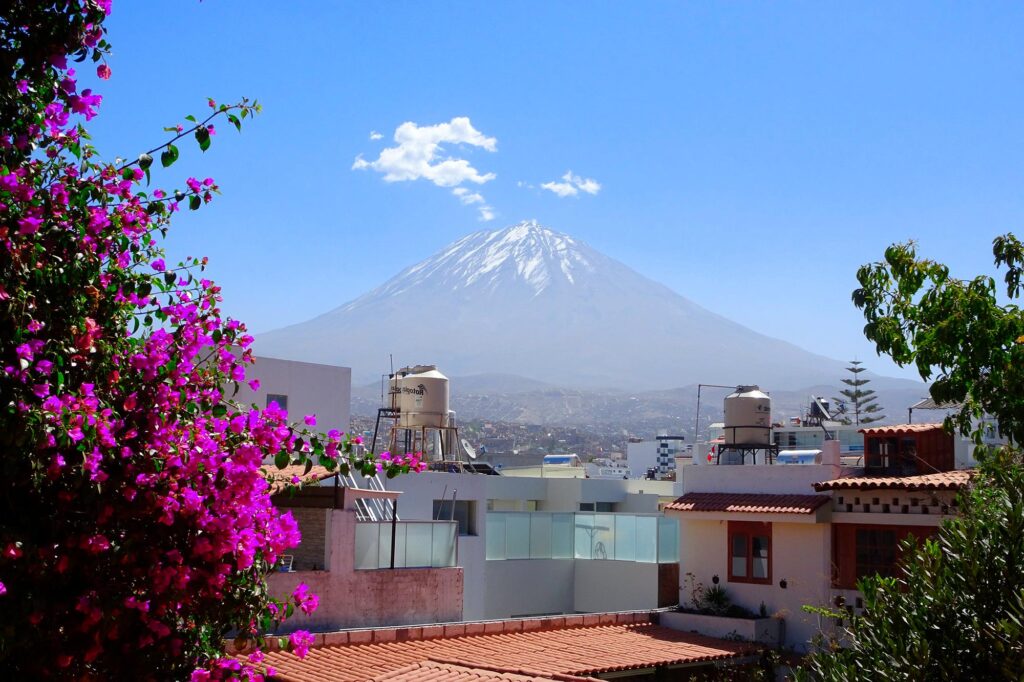

Location and Access to Misti Volcano
Misti Volcano is located in the Chili River Valley, in the Arequipa region, about 18 kilometers from the city. It’s not the only volcano in the area nearby you’ll also find Chachani and Pichu Picchu. Its proximity to the city makes it an ideal destination for those seeking a high-altitude hiking adventure. Access is relatively easy, as off-road vehicles can reach the base, where the hike to the summit begins.
Elevation and Geography of Misti Volcano
Located at over 2,400 meters above sea level and reaching a maximum elevation of 5,882 meters, Misti is one of the tallest volcanoes in Peru—a true challenge for climbers. During the ascent, you’ll encounter various terrain types, from arid zones at the base to rocky and volcanic ash areas near the summit. In winter, the peak is often covered in snow, adding beauty to its landscape.
History and Cultural Significance of Misti Volcano
Experts say Misti is around 800,000 years old. About 2,000 years ago, it experienced one of its major eruptions—a level 5 on the volcanic scale (from 0 to 8)—which was considered one of the most significant events in southern Peru at the time.
Over the last 50,000 years, Misti has had at least 12 eruptions, with volcanic deposits covering much of the area that is now the city of Arequipa. One major eruption occurred during the 15th century, in Inca times, when it was referred to as “apu” (lord) for its greatness and divinity. It’s said that when the eruption occurred, Inca ruler Tupac Yupanqui offered prayers and sacrifices to calm the volcano’s fury—but without success.
Today, Misti remains a strong symbol for Arequipa’s residents, and its image appears in many aspects of daily life.
In the Quechua language, Misti means “lord of the white race.”
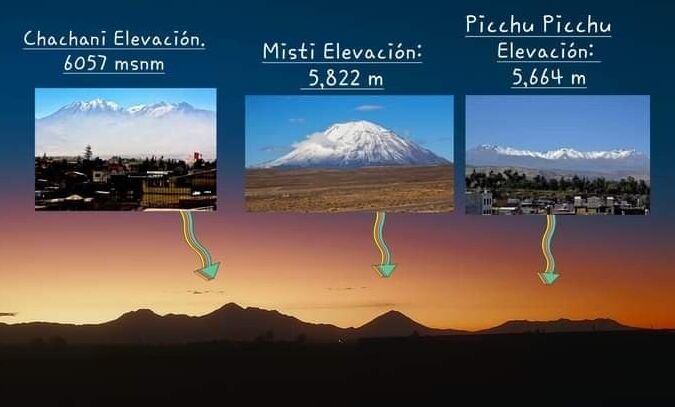
Comparison: Misti vs. Other Famous Volcanoes
Compared to other volcanoes, Misti stands out due to its massive size and is considered one of the largest in Peru. It is often compared to South America’s famous volcanoes like Cotopaxi in Ecuador and Villarrica in Chile. However, Misti’s proximity to a major city like Arequipa and its accessibility set it apart. Though it is not as tall as some of these volcanoes, Misti offers a unique experience due to its cultural symbolism and panoramic views of Arequipa and surrounding peaks such as Chachani and Pichu Picchu.
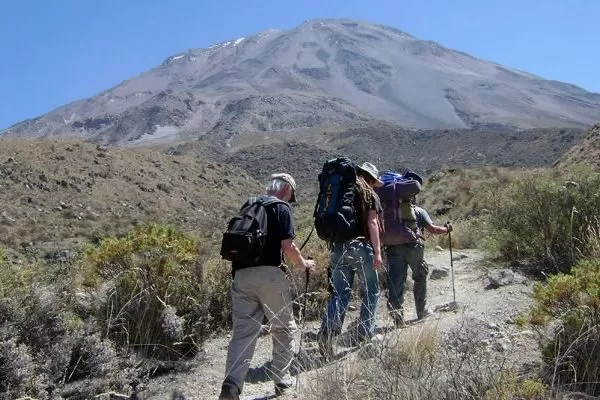
How to Get to Misti Volcano from Arequipa
To get to Misti from the city of Arequipa, the best option is to hire private transport or a guided tour that includes transportation to the base. Many local tour companies offer this service, making it easy for visitors to start their climb. These tours often include 4×4 vehicles, mountain gear, and a specialized guide.
You can also rent a car, but be aware that the route is challenging, and it’s highly recommended to have a local guide. Another option is to hike from the town of Chiguata or from the Aguada Blanca National Reserve.

Weather and Best Time to Visit Misti Volcano
Weather at Misti varies greatly depending on the time of year. The best time to visit is during the dry season, from May to September, when there’s less rain and more stable conditions. Temperatures during this season range from 20 °C at the base to -5 °C at the summit, especially early in the morning. In the rainy season (October to April), the climb becomes more difficult due to mud and fog, which can reduce visibility.
Tips for Visiting Misti Volcano
It’s important to take a few things into consideration when visiting the volcano.
What to Bring to Visit Misti Volcano
To enjoy a safe and comfortable climb, be sure to bring the proper gear. Here’s a list of essentials:
- Layered warm clothing, temperatures drop as you ascend, so wear layers you can adjust.
- Sun protection, bring sunscreen, a hat, and sunglasses due to intense sun exposure.
- Trekking boots, terrain is rocky and unstable, so sturdy boots are essential.
- Gloves and a hat, temperatures are very low at the summit, so dress accordingly.
- Trekking poles, to help with balance and reduce leg strain during the hike.
- Water and snacks, stay hydrated and energized throughout the ascent.
Hiking Route and Recommendations
The most popular hiking route begins from Chiguata or the Aguada Blanca National Reserve, or from a point called “Pastores.” The hike usually lasts about two days, including a night of camping near the summit. The first day includes a trek to base camp, and on the second day, the climb is completed at dawn to enjoy sunrise views.
It’s highly recommended to go with a local guide, as the altitude and weather can be challenging. Guides know the terrain well and can provide tips to manage altitude sickness, which is common at these elevations.
Entrance Fees and Other Costs
No specific entrance ticket is required to visit Misti, but most costs are related to gear and guiding services. Guided tours typically range from $80 to $150 USD per person and include transport, basic mountain gear, meals, and camping equipment.




